
CyanthOx™ Hippophe Rhamnoides Extract (50% PAC)
As we age, our cells need to stay healthy for us to feel our best, but ageing can slow them down, leading to tiredness and weakened immunity. CyanthOx™ Hippophe Rhamnoides Extract (50% PAC) is a powerful plant-based antioxidant that surpasses traditional extracts. It can significantly boost cellular health. A clinical study recently published in Clinical Interventions in Aging shows that CyanthOx™ stimulate 3 different types of stem cell, contributing to anti-aging, anti-inflammation, skin health, vessel health and blood circulation.
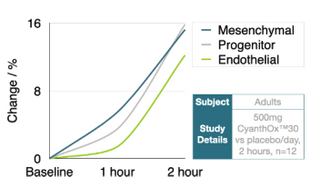
Design: A randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blinded, cross-over trial was conducted with 12 participants for 2 hours.
Serving Size: 500mg CyanthOx™ per day
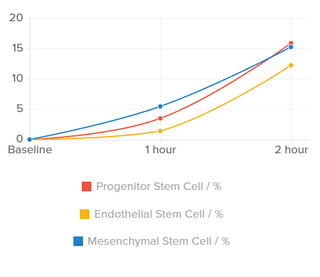
Result: Consumption of sea buckthorn proanthocyanidins leads to an increase in the following stem cells: the result after 2 hours of consuming two capsules is below.
- Progenitor stem cell
- Endothelial stem cell
- Mesenchymal stromal cell
Conclusion: 500mg CyanthOx™ (150mg sea buckthorn proanthocyanidins) stimulates 3 different types of stem cells and supports preventive health, regenerative health, and postponing the ageing process.*
(Drapeau, Benson and Jensen, 2019)
Key Benefits of CyanthOx™:
- Cell Regeneration: Increases stem cell release by 40%, aiding in the repair of damaged tissues.
- Boosts Nitric Oxide: Raises nitric oxide by 96% in cells, improving blood flow and oxygen levels for better cell function.
- Enhances Mitochondrial Health: Boosts mitochondrial mass by 69% and doubles ATP production, energizing cells from within.
- Stronger Antioxidant Protection: Increases SOD production by 11%, combating oxidative stress and promoting more prolonged cell health.
- Superior Free Radical Defense: Outperforms common antioxidants, offering better protection against cell damage.
By enhancing cell regeneration, nitric oxide levels, and mitochondrial function, and by combating oxidative stress, CyanthOx™ promotes healthy ageing and vitality.
CyanthOx™ is extracted from an ancient plant grown in Tibetan Plateau called sea buckthorn. Through millions of years of evolution, sea buckthorn is a treasure of bioactive nutrients. CyanthOx™ water-soluble extract is a unique and rich combination of polyphenols, proanthocyanidins, and bioflavonoids, which offer extensive natural health benefits.
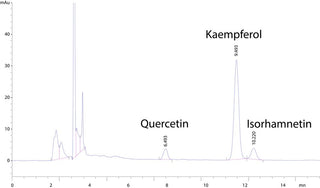
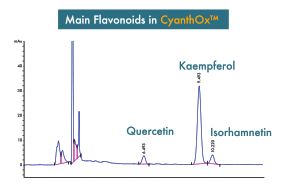
Shown by the HPLC on the right, the main flavonoids found in CyanthOx™ are: Quercetin, Kaempferol & Isorhamnetin
As a result of its rich antioxidant profile, CyanthOx™ is very potent in terms of antioxidant capability.
According to Oxygen Radical Absorbance Capacity (ORAC) analysis*, CyanthOx™ has an ORAC value of 895,281 μmol TE/100g (Puredia Corporation Limited, 2019).
In comparison, CyanthOx™ is 8 times stronger than grape seed extract (Superfoodly.com, 2019) and 1.7 times more potent french maritime pine bark extract (Legault et al., 2013).
A clinical study recently published in Clinical Interventions in Aging shows that CyanthOx™30 may stimulate 3 different types of stem cell, contributing to anti-aging, anti-inflammation, skin health, vessel health and blood circulation.
Design: Randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blinded, cross-over trial was conducted in 12 participants for 2 hours.
Serving Size: 500mg CyanthOx™30 per day
Result: Consumption of sea buckthorn proanthocyanidins leads to an increase in the following stem cells:
- Progenitor stem cell
- Endothelial stem cell
- Mesenchymal stromal cell
Conclusion: 500mg CyanthOx™30 (150mg sea buckthorn proanthocyanidins) stimulates 3 different types of stem cell and supports preventive health, regenerative health, and postponing the aging process.
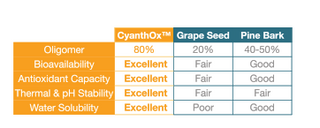
Unique Blend of Polyphenols
Higher concentration, better bioavailability, robust antioxidant capability, excellent stability, and solubility make CyanthOx™ stand out. In particular, most of the oligomers in CyanthOx™ are dimers and trimers, leading to better antioxidant ability than monomers and polymers.


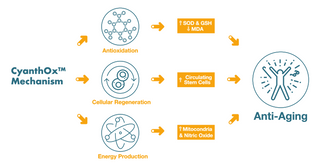

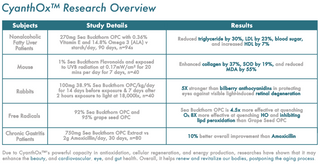
Clinical Trial
Antioxidation
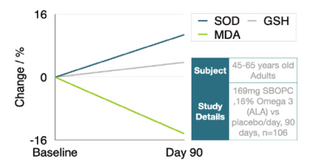
Sea Buckthorn Proanthocyanidins was shown to
increase SOD by 11%, GSH by 4%, and reduce
MDA by 15%.
Cellular Health
CyanthOx™ was shown to stimulate circulating
stem cells (Mesenchymal, Progenitor, and Endothelial) in our bodies by over 40% within 2 hours
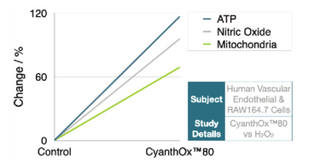
Energy
CyanthOx™ was shown to enhance ATP by
117%, Nitric Oxide by 96%, and Mitochondrial
Mass by 69%.
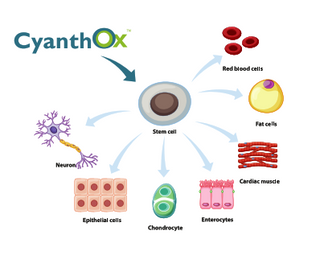
"Stem cells serve as a sort of internal repair
system, with the potential to become another
type of cell with a more specialized function such
as a muscle cell, a red blood cell, or a brain
cell."
National Institutes of Health (NIH)
As our body ages, the number of stem cells
decreases drastically. With less circulating stem
cells, fewer stem cells are available to migrate
into damaged tissues to aid the renewal process.
The development of degenerative health
problems has been linked to a lower number of
circulating stem cells. Hence, increasing the
number of circulating stem cells increases the
bodyʼs ability to repair and maintain optimal
health.

Research Links
- Puredia Corporation Limited. (2019). CyanthOx™80 ORAC Analytical Report. Available at: Here.
- Superfoodly.com. (2019). Antioxidant ORAC Value: Grape Seed Extract. [online] Available at: https://www.superfoodly.com/orac-value/grape-seed-extract/.
- Legault, J., Girard-Lalancette, K., Dufour, D. and Pichette, A. (2013). Antioxidant Potential of Bark Extracts from Boreal Forest Conifers. Antioxidants, [online] 2(3), pp.77-89. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4665433/.
- Drapeau, C., Benson, K. and Jensen, G. (2019). Rapid and selective mobilization of specific stem cell types after consumption of a polyphenol-rich extract from sea buckthorn berries (Hippophae) in healthy human subjects. Clinical Interventions in Aging, [online] Volume 14, pp.253-263. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6368418/.
- Sugimura, R., Jha, D., Han, A., Soria-Valles, C., da Rocha, E., Lu, Y., Goettel, J., Serrao, E., Rowe, R., Malleshaiah, M., Wong, I., Sousa, P., Zhu, T., Ditadi, A., Keller, G., Engelman, A., Snapper, S., Doulatov, S. and Daley, G. (2017). Haematopoietic stem and progenitor cells from human pluripotent stem cells. Nature, [online] 545(7655), pp.432-438. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28514439.
- Yoder, M. (2017). Endothelial stem and progenitor cells (stem cells): (2017 Grover Conference Series). Pulmonary Circulation, [online] 8(1), p.204589321774395. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5731724/.
- Goldberg, A., Mitchell, K., Soans, J., Kim, L. and Zaidi, R. (2017). The use of mesenchymal stem cells for cartilage repair and regeneration: a systematic review. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research, [online] 12(1). Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28279182.
- Keating, A. (2006). Mesenchymal stromal cells. Current Opinion in Hematology, [online] 13(6), pp.419-425. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3365862/.
